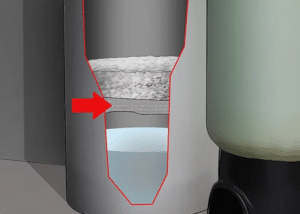
Hard water is when there are too many minerals in the water. These minerals are not necessarily life-threatening but tend to cause issues in your home. Does your bathtub have streaks or spots, or do your drinking cups? What about your hair and skin—do they feel dull, sticky, or itchy?
A water softener is a filtration system that removes magnesium, calcium, and other causes of hard water. Simply put, when water flows through this filter, the hard minerals are removed, and the water is softened enough to flow through plumbing.
That could get caused by hard water. So we know what causes hard water and how to fix it, but how does the filtration system work?

How It Works
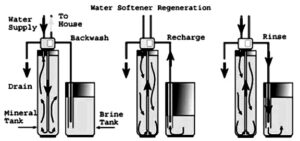
A water softener is a system that removes both magnesium and calcium from your water by exchanging ions. Hard water causes scales to build up on appliances and in your pipes and can clog them and decrease the water system pressure.
Essentially, scaling gets created when the calcium and magnesium solidify as pipes heat. If you have a hard water issue, your water heater will sound like it is popping, similar to the sound you hear when popping popcorn.
With the process of ion exchange, the hard water is placed in a mineral-rich tank and flows through a spherical resin bead bed. These plastic beads get a charge from sodium ions– the beads have a negative charge. The minerals that are causing issues are positively charged.
The phrase ‘opposites attract’ applies here, as the beads will attract the minerals. Because the magnesium and calcium are attracted to the resin beads, they get removed from the water, and soft water can be released into your home.
When To Add Salt To Water Softener
Salt is crucial to your water softeners’ ability to function. Without salt, ion-based exchange systems cannot work, and the hard water will remain hard. There are a few factors that determine how much salt you need, the type of salt, and, of course, how to know when you need more salt.
Generally, you’ll want to add salt if you look in your tank and check the bottom. If there’s less than a quarter of a tank’s worth of salt, you’ll need to add more.
How To Add Salt To Water Softener
You should remove the lid of your brine tank and look inside. If you see water at the bottom of the tank, then you’ll need more salt! However, before you add new salt, make sure you take time to loosen anything dried to the sides of the tank.
You should then fill your tank to the halfway mark with salt. If you have sized your brine tank correctly, you should have an approximate amount of salt you’ll use each year and an approximate idea of how often to check and add more salt.
How Much Salt Is Enough?
Knowing how much salt and what types of salt to use is just one part of the equation when dealing with an ion-exchange filtration system. The salt in these systems makes your water soft, ensuring lower levels of calcium and magnesium than hard water.
The amount of salt used varies, and the type is crucial. Some salts are not the best salt for use, while others are better but more expensive.
Things that determine how much salt to use:
- Type of water softener system
. - Size of the brine tank
. - Water hardness, on average
. - Household water usage
.
What is the Best Type of Water Softener Salt to Use?
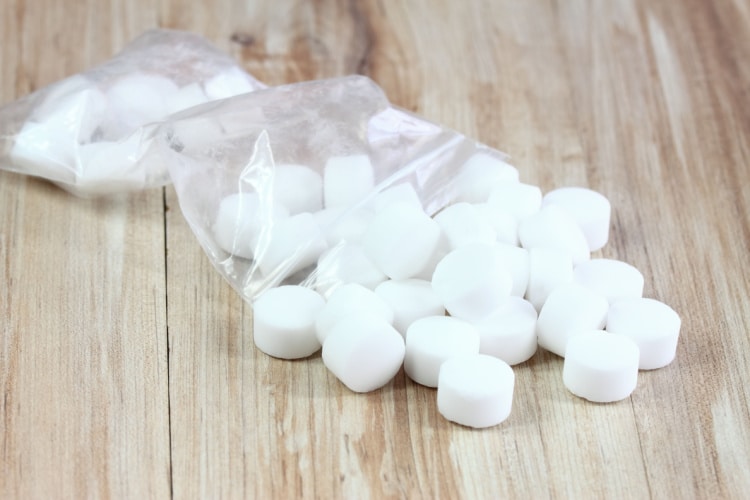

There are three basic types of salt for water softeners: rock salt, solar salt, and evaporated salt. Choosing the best salt for your system will depend on a few things.
Rock Salt
Rock salt is the least expensive, but it has a higher level of minerals and impurities that are not soluble. That can cause a muddy tank and decrease the tank’s ability to soften the water. That is because rock salt has a high amount of calcium sulfate, which affects its purity.
Solar Salt
Solar salt has more solubility than rock salt. Solar Salt is obtained by evaporating seawater and has pellet and crystallized forms. You might get solar salt from the Great Salt Lake or San Francisco Bay. The water is pulled into very shallow ponds, evaporated, and then the sale is gathered.
Evaporated Salt
The highest quality softener salt is evaporated salt. Evaporated salt gets made by mining and evaporating the salt, and the purest salt available in this form is 99.99% sodium chloride. These crystals are then processed using a drying and screening process to ensure their purity before it’s turned into pellets.
What Happens if a Water Softener Runs Out of Salt?

When using an ion-based exchange system such as water softeners, you must know two common issues may surface. These issues are salt bridges and salt mushing. Both will get explained below.
Bridging
You should always keep an eye on whether you have a salt bridge forming. Salt bridges are not good, and your inspection rounds should be every two months. If a salt bridge has occurred, your brine tank will not seem like it’s using salt, and the salt level will not change after months of use.
Salt bridging often gets caused by high humidity or if you’re using the wrong type of salt for your system. A salt bridge is a space created out of salt that separates water and salt.
Mushing
Salt mushing is a more serious issue when dissolved salt recrystallizes and forms sludge in the bottom of your brine tank. This thick layer of salt will keep your water softener from cycling. If you have a mushing problem, your water will be hard, and your brine tank will be useless.
Checking if You Need Salt
Understanding the basic aspects of your water softener system will ensure the system you paid for lasts a long time. So, let’s dive into how to check if you need salt and how often to add salt to your tanks.
Account for Softeners’ Age
If your softener is an older model, you will use more salt than a newer model. That is because your system isn’t as up-to-date as the newer models. So if your softener is older, you’ll need more salt and frequent check-ups.
How Much Salt To Add
Your brine tank should be at least one-quarter full of salt at all times. It should never get filled to the top because that can affect performance. The salt level should remain a few inches above the natural water level.
When you add too much salt, you’ll cause bridging or mushing, which builds up in your system and affects the quality of your water.
Conclusion
Water softeners get used more frequently these days, as hard water is a problem for a lot of folks. However, not everyone knows how often to refill their salt or how to use their system. You should know two common issues can occur if your tank is used incorrectly or filled with the wrong amount of salt.
Mushing and bridging happen occasionally but are easy to correct and avoid. Simply ensure you’re following the owner’s guide of your system, and ask for help if you need it. Ensure that you are using the best kind of salt that you can—while not everyone can afford solar salt or evaporated salt, those are better than rock salt.
Consider the benefits of solar or evaporated salt over the cons of rock salt before purchasing and using rock salt in your brine.