When it comes to selecting a water softener for your home, most homeowners choose sodium chloride. However, another primary option that you can select would be potassium chloride. When comparing the two, both solutions aim to soften water by ion exchange. However, even though they serve the same purpose, they have several differences.
Are you wondering whether a potassium chloride water softener salt vs. sodium chloride water softener is right for you? In this guide, we will review the key differences between these softeners.
What Is a Water Softener?
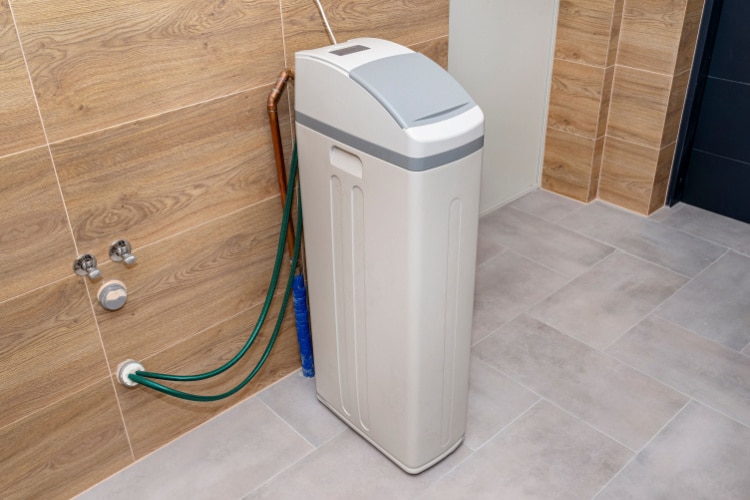

A water softener is a type of filtration system that helps to remove highly concentrated properties such as calcium and magnesium that produces hard water. The purpose of having a water softener system for your home is to filter out the minerals that make up hard water and reduce buildup within your plumbing.
Typically, what is filtered through your water softener system is called regenerant.
What Is Regenerant?
Regenerant is a chemical solution used to restore ion exchange resin to its fully ionic form. For instance, sodium chloride water softener is a regenerant typically used for water softener ion exchange.
From here, this solution then regenerates cation exchange water softeners. Before figuring out whether or not to use potassium chloride or sodium chloride regenerant, it’s essential to know its process.
How Does It Work?
When it comes to the process of a water softener system, aside from regenerant playing a pivotal role, the primary goal is to eliminate and filter out hard water. The system does that by removing hard water as it enters through the main pipe of your home with the help of resin beads in the tank.
Then, after the resin beads hold onto the hard water and remove it, the softened water flows out of the tank and into your plumbing system.
The Differences Between Potassium Chloride Water Softener vs. Sodium

It’s often preferred to use sodium water softener over potassium chloride. Although they share the same purpose, they’re entirely different when it comes to health and the environment.
How Much Is Water Softener Used?
When considering the amount of water softener used for these solutions, even if both are effective in performance, potassium chloride requires more than if you were using sodium chloride water softener.
Does It Have an Impact on My Health?
When it comes to health benefits, potassium chloride is better suited to avoid high levels of salt that come with sodium chloride. Since potassium chloride has potassium, it’s a vital nutrient that helps if you have issues with your renal or kidney. It also helps if you’re on a low-sodium diet as it minimizes sodium content from regenerated water.
Is It Eco-Friendly?
If you’re looking for a regenerant that is beneficial for the environment, potassium chloride water softener is the leading contender. One of the reasons why is that it’s easily disposable, and since one of the components in this solution is potassium, it helps grow plants.
What Is the Cost?
One of the downsides to acquiring potassium chloride water softeners rather than sodium is its cost. Potassium chloride’s cost is significantly higher, especially considering the price, brand, and where you purchase it. You also have to consider the quality as well.
This higher price is generally because of the amount it takes to soften water. Sodium chloride, however, only needs one bag to soften water.
Potassium Chloride Water Softener Benefits
Though the primary downsides of acquiring potassium chloride for your water softener system are cost and the amount used, there are various benefits.
- It’s Beneficial for Your Health: It’s worth noting that since this type of water softener is composed of potassium, once consumed, it helps maintain a healthy amount of fluids in your body. It also helps decrease your risk of high blood pressure.
- It Helps Out the Environment: One of the primary nutrients for plant growth is potassium, and a healthy amount of it can enhance soil stability.
- It Reduces Sodium Impact: Too much sodium can be overwhelming and costly for your water softener system. Using potassium chloride reduces that.
Sodium Water Softener Salt Benefits
Although some might prefer potassium chloride, if you’re looking for a water softener on a budget, sodium chloride might be the right one for you.
- Reduces Buildup: Incorporating sodium chloride for your water softener reduces mineral and sediment buildup in your plumbing.
- Minimizes Calcium Damage: Sodium water softener breaks down and reduces calcium buildup.
- Cost Effective: Sodium chloride water softener is significantly less expensive than potassium chloride solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are you still wondering which is best between potassium chloride water softener salt vs. sodium? Here are some frequently asked questions about this topic.
Is it safe to mix both potassium and sodium chloride water softeners?
It is safe to mix both potassium and sodium chloride water softeners. Even if you mix them together, the combined solution will still undergo the same regeneration process.
What do I do if I want to switch from sodium chloride to potassium chloride water softener?
It is safe to switch from sodium chloride to potassium chloride. Even though both have different properties, they have the same purpose: reducing or removing resin within the tank.
Which water softener is good for plants?
Potassium chloride is the ideal option if you’re looking for an eco-friendly water softener. This solution has potassium, one of the key nutrients helping plants grow.
Final Thoughts: How To Know if Potassium Chloride or Sodium Chloride Water Softener Is Suitable for You
While potassium chloride water softener salt vs. sodium chloride water softener are fantastic options, sodium chloride is more efficient as it’s more economically sound.
Aside from being cost-effective, sodium chloride also reduces calcium damage and sediment buildup. Though, if you’re looking for a more environmentally friendly water softener with health benefits, we recommend selecting potassium chloride.



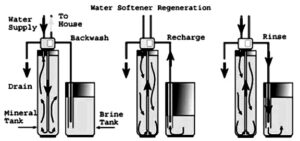

How about the opposite? Is it safe to switch from potassium chloride to sodium chloride? That is different from mixing the two.
And if a switch is made, does the regeneration flow time (or frequency) need to be adjusted?
Hi Bob, the opposite is usually not true. Manufacturers may utilize different media and/or techniques in salt-free systems that preclude the use of salt. Please check with your preferred manufacturer system to be sure.