When it comes down to water conditioner and water softener, a water conditioner removes harmful impurities, is inexpensive and low maintenance, and prevents hard water deposits. If your residential area has hard water, but you know the water is clean, a water softener should do the job just fine. In contrast, if you know your water is chemical-laden, or if you aren’t sure, you may want to choose a water conditioner instead.
Difference Between Water Conditioner and Water Softener
The main difference between water conditioner and softener is that water conditioner prevents limescale buildup by crystallizing calcium and magnesium minerals, while water softener removes hard water minerals through salt.
Water conditioners and water softeners work in similar ways in that they each affect the water’s composition. One notable distinction between the two is that a water conditioner doesn’t require salt to do its job.
| Water Softener | Water Conditioner |
|---|---|
| Removes hard water minerals | Crystallizes hard water minerals |
| Works on Ion-exchange technology | Works on Template-assisted Crystallization (TAC) technology |
| Requires frequent maintenance | Requires less frequent maintenance |
| Requires electricity | Does not require electricity |
What is a Water Conditioner?
Water conditioner is a device that is used to treat hard water by crystallizing calcium and magnesium minerals to prevent them from building up/sticking together. It is also sometimes called a salt-free water softener.
A regular water conditioner does not remove the minerals in hard water. But the minerals that cause the hard water are elementally changed, so the process still helps prevent scale buildup in your pipes and fixtures. Over time, the conditioner’s filter will need to be replaced.
There are several different types of water conditioners available, each composed of different workings but all reaching similar results.
Electromagnetic Water Conditioners
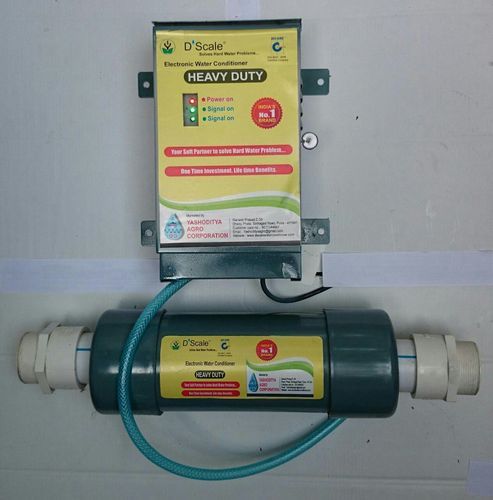

In this type of water conditioner, the molecules in the water are agitated by either magnets or wires which are installed on your home’s water pipes. Agitating the water causes a break-up of the molecules, reducing the calcium saturation of its ions. The breaking up process purifies the water and helps prevent scaling, but it does not soften the water. There is some controversy as to whether these methods are scientifically provable.
Catalytic Media Water Conditioners

This kind of water conditioner is like a salt-free water softener. A process called template-assisted crystallization (TAC) changes the composition of the minerals, keeping them from attaching on their way through the pipes. TAC will not soften your water, per se, but if you have well water, this type of conditioner is a good choice.
Water Softeners

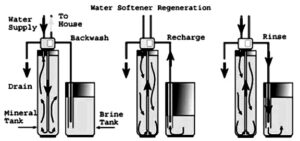
A water softener runs on a simple concept: water filters through positively charged resin beads which grab the negatively charged minerals, releasing sodium ions in their place. The resin beads also help flush the softener system of the captured minerals.
As a result, the water will be softer and not accumulate in your pipes and fixtures. However, water softeners do not filter the water. Water softeners are more expensive than water conditioners, require salt replacement and maintenance regularly, and have a wastewater footprint.